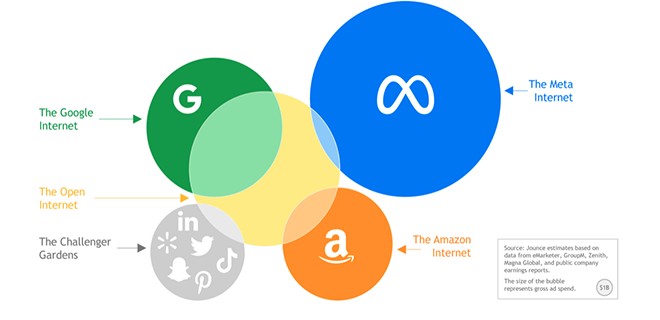
Over the past five years, we’ve watched walled gardens flourish while the open internet faces increasingly challenging conditions. By the end of this year, Google, Amazon, and The Trade Desk will control over 60% of the open Internet ad spend.
In Jounce Media’s annual report, ‘The State of the Open Internet,’ three influential market forces shed light on the obstacles that media companies and advertising technology platforms face: demand concentration, bidstream bloat, and bidstream blindspots.
How can we level the playing field between the dominant walled gardens and the rest of the open internet? Of course, achieving this equilibrium is no simple task. Open Internet media companies and their ad tech counterparts are caught between the short-term financial obligation to contribute to bidstream bloat and the long-term financial goal of transitioning to two-sided marketplaces that unlock privileged data access.
Buy Side Chronicles and the Rise of the New Walled Garden
Walled gardens are experiencing a notable surge in their influence and evolving models.
“Over time, marketers pour more and more money into the walled gardens, which makes them critical business partners to bring demand to the open internet,” Chris Kane explained. “They have allocated almost 100% of their net new digital spend each year to walled gardens like YouTube, Meta, Pinterest, Snapchat, and Tik Tok to name a few. By controlling huge pools of demand, these companies are extremely well positioned to build DSP-like offsite advertising businesses.”
In the past couple of years, we’ve witnessed the emergence of at least 12 new commerce businesses adopting the walled garden model for their advertising products. Brands like Doordash, Etsy, Instacart, Uber, and Walgreens have all ventured into this sub-sector. We all know about Netflix’s newly launched walled garden and CVS, as well as other legacy open internet media businesses are now operating as sub-scale walled gardens.
In the future, it’s looking like most media companies will succeed in the open internet while utilizing third-party advertising platforms that produce billions of dollars of demand. Obviously,the best-fit platforms for aggregating demand are the walled gardens.
Over half of the $85B deployed by advertisers to the open internet in 2023 is expected to flow through walled garden buying systems. Walled gardens aren’t sellers on the open internet; they have become the largest buyers, wielding considerable influence.
Boo to Bidstream Bloats
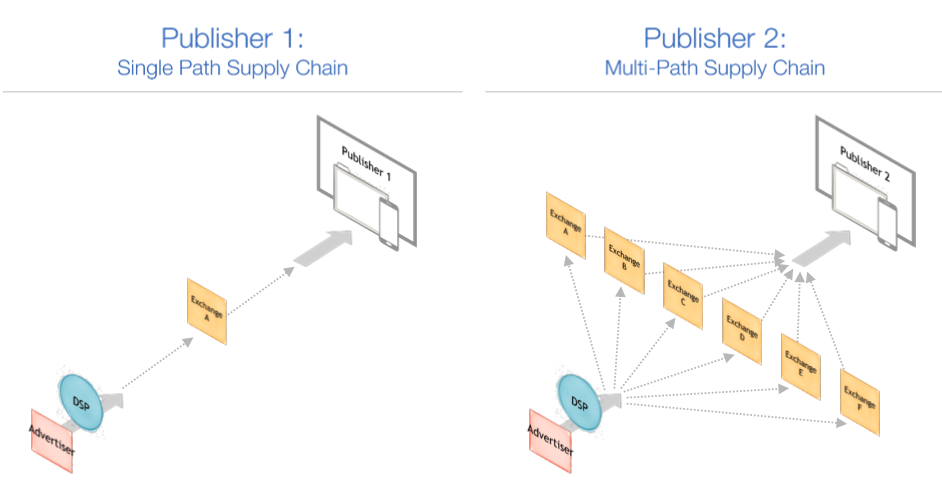
Publishers’ success in acquiring programmatic demand is driven by their ability to secure a significant share of the bidstream, a phenomenon called “volume bias.” This bias arises when DSPs allocate investments based on the number of auctions conducted. Now, here’s where the bloat comes in, and yes, I am referring to what your stomach looks and feels like after three slices of pizza.
Aside from the volume bias and non-exclusive monetization partnerships, publishers contribute to auction duplication in two ways:
Multi-Integrations: Publishers initiate auctions through multiple integration points with various exchanges. They may simultaneously employ Prebid, Amazon Publisher Services, and Google Open Bidding. Consequently, DSPs receive three bid requests from each ad exchange for every available impression.
Rebroadcasting: This primarily applies to mobile and CTV publishers and involves multiplying bid requests through reselling. A publisher collaborates with an ad network, enabling these networks to source DSP demand by reselling ad exchanges. Ultimately, the DSP gets five or more resold bid requests from each ad network for each impression.
Along with the bidstreams bellies getting too bloated, publishers reap all the benefits of ballooning auction volume. Still, the ad tech companies doing all the work are paying for it and only generating revenue when the impression is filled at the end of the process.
Eliminating Bidstream Blindspots and Keys to Future Successes
Jounce Media’s State of the Internet report reveals that buyers now have greater access to information about ad placement, thanks to industry initiatives focused on transparency within the supply chain, such as ads.txt and sellers.json.
While buyers can now verify the authenticity of available inventory, review complete payment histories, and identify the highest value of ad placements, their ability to make bidding decisions based on audience and content continues to go downhill thanks to privacy regulations, platform policies, and media buying decisions.
“CTV content blindspots area business choice. Media companies are looking to maintain control of advertising budgets,” Kane explained. “Although it would be desirable for publishers to collaborate and establish standards while forging deep partnerships with one or possibly two exchanges, the likelihood of this occurring is quite low.”
Bidstream filtering is also getting worse. Publishers are increasingly conscious of traffic shaping and consequently required to submit duplicate requests. Kane strongly emphasizes the need for change to originate from the buy side, urging buyer behavior to evolve and DSPs to take assertive actions before it becomes too late.
You can explore the full report here to delve deeper into these findings.